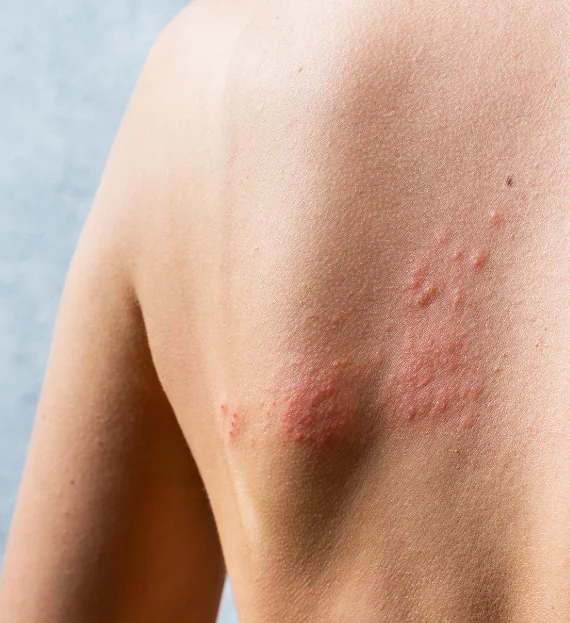
Urticaria
Urticaria is a skin condition where rashes appear in groups as a response to some triggering factor, commonly called as “hives”. These responses are by one’s own immune system. Sometimes these rashes are filled with watery fluid and vary in shape and size. These water-filled bumps/welts can be present for a few hours to a few days.
The allergen or the triggering factor for urticaria can be certain food items or preservatives in packed food, insect bite/stings, medication, infection, physical stimuli like clothes, heat, light rays, pressure, etc.
Urticaria can be treated with topical as well as oral medications. Topical creams/ointment or lotions are prescribed to control inflammation and relieve itching. Oral medications like antihistamines are also prescribed to relieve itching and control allergic reactions. In severe cases, epinephrine is given to counteract life-threatening allergic reactions.
Dermatologists evaluate and treat the urticaria with appropriate treatment and suggest skin care tips at a personal level.
Faq
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Urticaria is the body’s response to particular allergy-causing factors appearing as skin rashes and this response varies from person to person. The rashes appear in groups, red, itchy, and sometimes fluid-filled. It is commonly called as “Hives”.
A. The sign and symptoms of urticaria are the appearance of raised itchy rashes which are red, painful, and welt/bumps in any part of the body. The size and shape of the welt/bumps vary and might be present for a few hours to a few days.
A. Urticaria is treated with anti-histamines which help in relieving itching and reducing the swelling whereas corticosteroids are prescribed to control the inflammation. In some severe cases, epinephrine is prescribed to manage the life-threatening allergic reaction. Moreover, one must also follow preventive measures like avoiding the triggering/causative factors for the prevention of any future episodes of urticaria
A. Those who are aware of the causative triggering factors of urticaria can prevent it by avoiding those triggering factors. The triggering factors or allergens can be environmental, specific food, or medications. In most of the urticaria cases, the causative factor in not known.
A. No. Urticaria does not spread to other body parts or to other persons. It’s a non-contagious condition where the person’s immune system responds to the trigger which does not get transmitted from person to person.