Human papilloma virus infections
A group of 100 related viruses are collectively called Human Papillomavirus (HPV) whose infection causes dreaded diseases like warts or cancer. It is also considered to one of the leading causes for cervical cancer in females.
HPV is highly contagious, spreading through sexual activity where the infected person is unaware of the infection or transmission as they remain asymptomatic even after few to many years. Mother-to-be female can pass on the infection to infant during the normal vaginal delivery.
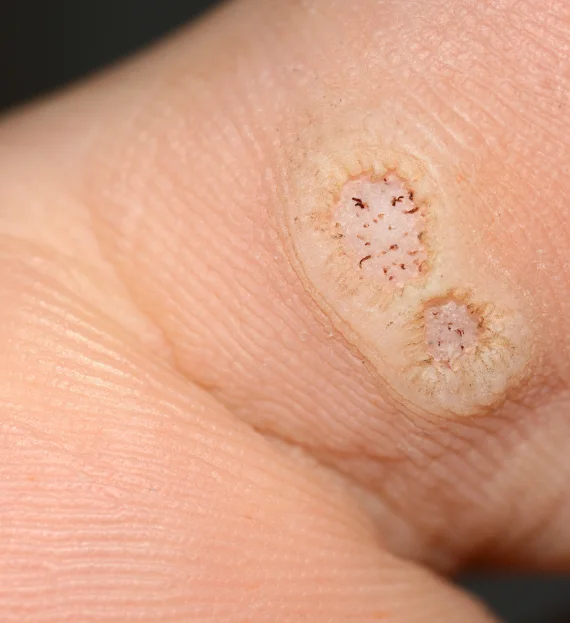
Some of the HPV can cause warts on hands, feet, and genitals while some cause cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina in females and penis, anus in males. It can also cause oral or throat cancer.
HPV-related warts are treated like any other warts with topical medication, freezing/burning, or surgical procedure whereas the cancer is treated in multiple ways as per the need.
As a preventive measure, healthcare providers recommend the HPV vaccines in the pre-teen years of both males and females before they get active sexually. Some of the laboratory tests like PAP test by females and HPV tests are recommended to be conducted at regular intervals in adulthood to detect HPV infection at the earliest.
Faq
Frequently Asked Questions
A: HPV is a group of more than 100 related viruses that can cause warts or lead to cancer, particularly cervical cancer in women.
A. HPV transmission happens through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity involving oral/anal or vaginal sex. It can also get transmitted from mothers to newborns during childbirth through normal vaginal delivery.
A. HPV-related diseases cannot be cured. Vaccines are available as one of the effective preventive measures against HPV infection. It gives protection against the most common cancer-causing viruses.
A. HPV-related warts are treated with multiple options like – topical medications, freezing or burning warts, electrocautery, or surgical excision of warts.
A. In most cases, HPV infection does not show up any symptoms nor does the infected person know about their own infection. It gets presented as warts on feet, hands, and genitals, or as cancer of the vagina, penis, cervix, anus, or throat in others.
A. HPV-related cancer is treated in multiple ways like – surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these treatments.
- One can prevent HPV infection by following the steps –
- Vaccination in pre-teens
- Practicing safe sex
Undertaking tests at regular tests like PAP tests by females and HPV tests by males
Although HPV vaccines are recommended for both males and females but preferred to be vaccinated in the preteen years – 9to12 years, or before the onset of sexual activity. People can also consider getting post-teen until the age of 26 years if not vaccinated earlier.